Bias in AI

I read an article from Rutgers University-Camden that begins by saying that most people now realize that artificial intelligence has become increasingly embedded in everyday life. This has created concerns. One of those lesser-spoken-about concerns is around bias in its programming. Here are some excerpts from the article.
Some AI tasks are so innocuous that users don't think about AI being involved. Your email uses it. Your online searches use it. That smart thermostat uses it. Are those uses frightening? But as its capabilities expand, so does its potential for wide-ranging impact.
Organizations and corporations have jumped on the opportunity presented by AI and Big Data to automate processes and increase the speed and accuracy of decisions large and small. Market research has found that 84 percent of C-suite executives believe they must leverage artificial intelligence to achieve their growth objectives. Three out of four believe that if they don't take advantage of AI in the next five years, they risk going out of business entirely.
Bias can cause artificial intelligence to make decisions that are systematically unfair to particular groups of people, and researchers have found this can cause real harm. The Rutgers–Camden researcher Iman Dehzangi, says that “Artificial intelligence and machine learning are poised to create valuable opportunities by automating or accelerating many different tasks and processes. One of the challenges, however, is to overcome potential pitfalls such as bias.”
What does biased AI do? It can give consistently different outputs for certain groups compared to others. It can discriminate based on race, gender, biological sex, nationality, social class, or many other factors.
Of course it is human beings who choose the data that algorithms use and humans have biases whether they are conscious of them or not.
"Because machine learning is dependent upon data, if the data is biased or flawed, the patterns discerned by the program and the decisions made as a result will be biased, too," said Dehzangi, pointing to a common saying in the tech industry: "garbage in, garbage out." “There is not a successful business in operation today that is not using AI and machine learning,” said Dehzangi. Whether it is making financial investments in the stock market, facilitating the product development life cycle, or maximizing inventory management, forward-thinking businesses are leveraging this new technology to remain competitive and ahead of the curve. However, if they fail to account for bias in these emerging technologies, they could fall even further behind, remaining mired in the flawed data of the past. Research has revealed that if care is not taken in the design and implementation of AI systems, longstanding social biases can be embedded in the systems' logic.
 It's not the metaverse. The fediverse is a network of interconnected social media servers from all over the world. Each server on the fediverse can be thought of as an independent platform with its users, content, and rules. Servers share information to enable people to connect and discover new things across the fediverse.
It's not the metaverse. The fediverse is a network of interconnected social media servers from all over the world. Each server on the fediverse can be thought of as an independent platform with its users, content, and rules. Servers share information to enable people to connect and discover new things across the fediverse.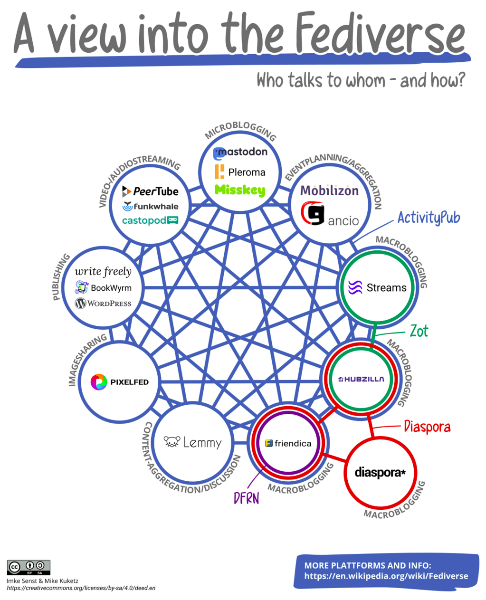
 Coursera’s CEO,
Coursera’s CEO,